Chapter 0: Preliminaries
To understand calculus, a student needs an excellent foundation in algebra, geometry, and trigonometry. In this chapter we review these topics and introduce the notation used in this text. From the basics of numbers to solving trigonometric equations, this chapter provides a comprehensive discussion necessary for success in calculus.
Sections
0.1 Fundamental Skills in Algebra
Solving one-variable equations and inequalities. Factoring algebraic expressions by extracting the greatest common factor (GCF) and by grouping. Factoring differences of squares, sums of cubes, and differences of cubes. Factoring \(x^2 + bx + c\) and \(ax^2 + bx + c.\) Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions with algebraic expressions. Polynomial division.0.2 Numbers, Sets, and Absolute Values
Classifying numbers as integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. Sets and using set notation. Defining intervals and using interval notation. Defining absolute values and solving equations and inequalities with absolute values. Introducing the \(xy\)-plane and coordinates. Pythagorean Theorem. Finding the midpoint of a line segment and distance between two points. Areas and arc lengths of circular sectors, with conversion between degrees and radians. Graphing circles, ellipses, and hyperbolas, with translations. Definition of a function, domain, and range. Interpreting functions in words, mathematically, graphically, and numerically. Even and odd functions.0.5 Linear Functions and Equations
Defining a linear function. Graphing linear functions and defining slope. Lines in slope-intercept form and point-slope form. Solving systems of linear equations.0.6 Modifying Functions; Inverse Functions
Combinations of functions, composite functions, and their domains. Transformations of functions and graphs. Defining inverse functions. Solving for inverse functions algebraically, with geometric interpretation.0.7 Quadratics
Quadratics in general, vertex, and intercept forms. Review of factoring, completing the square, the discriminant, and the Quadratic Formula. Classifying solution types; determining minima and maxima; and identifying defining features of parabolas: intercepts, axis of symmetry, and vertex.0.8 Trigonometry
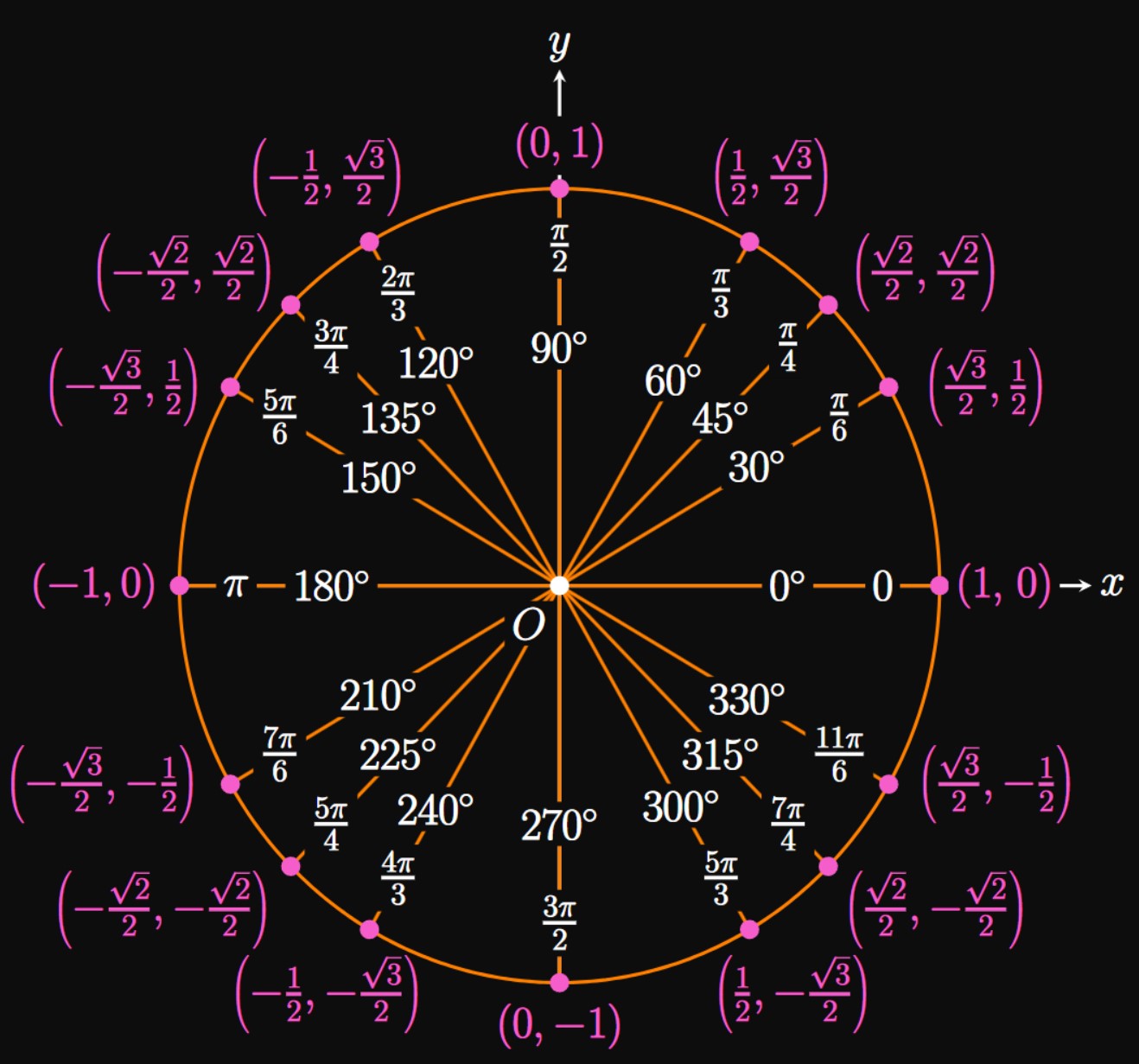
Overview of trigonometric functions and inverse trigonometric functions. Review of graphs, trigonometric identities, domain and range, and the Unit Circle. Solving trigonometric equations and simplifying trigonometric expressions. Law of Sines and Law of Cosines. Defining exponents and logarithms. Exponential and logarithmic functions. Introduction to the number \(e\) and its value. Laws of exponents and logarithms. Change of Base Formula. Solving equations with exponents and logarithms.0.10 Sigma Notation
Sigma notation to represent sums. Properties of summations. Formulas for evaluating simple series.